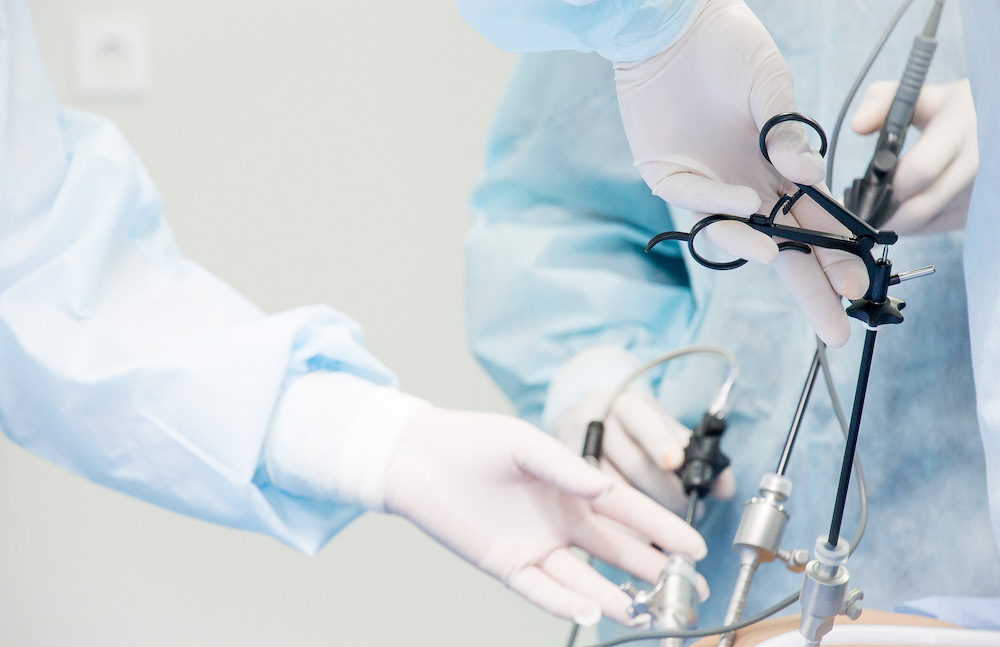
What is Laparoscopic Surgery (Minimally Invasive Surgery)?
**Laparoscopic Surgery**, also known as **Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS)**, is a modern medical technology that utilizes specialized instruments and a thin tube with a camera (Laparoscope) inserted through very small incisions, typically only 0.5–1 centimeter in size, instead of large open incisions. This method significantly reduces damage to surrounding tissues.
The Surgery Center at Thonburi-Chumphon Hospital recognizes the importance of highly efficient surgery. We utilize modern laparoscopic tools and technology to aid in diagnosis and treatment, ensuring patients receive the highest level of accuracy and care.
Open Abdominal Surgery VS Laparoscopic Surgery
| Factors to Consider | Open Abdominal Surgery | Laparoscopic Surgery |
|---|
| Amount of blood loss | 200–500 ml | 5–10 ml |
| Duration of surgery | More than 1 hour | More than 30 minutes |
| Incision size | 12–20 cm | 0.6–0.8 cm (3–4 incisions) |
| Post-operative pain | High | Low |
| Recovery time | 7–14 days | 2–5 days |
| Cost | Normal price | High price |
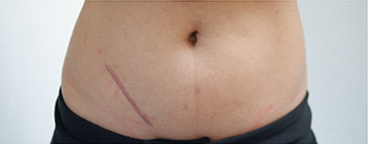
Open abdominal surgery scar
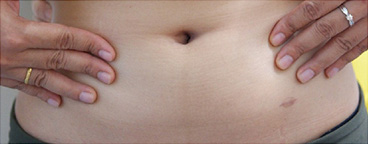
Laparoscopic surgery scar
Key Advantages of Laparoscopic Surgery
- Smaller Incisions and Less Pain: The minute size of the incisions leads to significantly reduced post-operative pain.
- Faster Recovery: Patients enjoy a shorter hospital stay and can return to work or daily activities much more quickly.
- Minimal Scarring: Scars are very small and fade easily, offering better cosmetic results.
- Reduced Risk: Decreases the risk of blood loss and post-operative complications, such as infection.
How Laparoscopic Surgery Works
During the operation, the surgeon gently inflates the abdomen with carbon dioxide gas (CO2) to create an expanded working space. The laparoscope and small surgical instruments are then inserted through 2–4 tiny incisions. The images from inside the body are transmitted to a high-resolution monitor, allowing the surgeon to see the internal organs clearly and perform the procedure with precision.
Common Conditions Treated with Laparoscopy
- Gallbladder Removal (Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy): Used for the treatment of gallstones.
- Appendix Removal (Laparoscopic Appendectomy): Used for the small-incision removal of an inflamed appendix.
- Hernia Repair: Can be used to repair inguinal or abdominal hernias using the keyhole technique.
- Gynecological Surgery: Such as hysterectomy (uterus removal) or ovarian cyst removal.
- Colorectal Surgery: Used to treat colon cancer or diverticulitis.
Preparation Before and After Surgery
Pre-Surgery Preparation
- Fasting: Fast from food and water for the period specified by the doctor, typically 6–8 hours before surgery.
- Medication Review: Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, or herbs you are currently taking.
- Body Preparation: Cleanse your body and follow your doctor's instructions for preparation.
Post-Surgery Care
- Pain Management: Take prescribed pain medication; pain typically decreases rapidly compared to open surgery.
- Incision Care: Keep the surgical site dry and clean, and monitor for signs of abnormality such as swelling, redness, or discharge.
- Mobility: Start walking slowly and gently to prevent complications and help the bowels resume function quickly.
- Activity Restriction: Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous exercise for 4–6 weeks as advised by your physician.